Algebraic Operations on Complex Numbers
In performing operations with complex numbers we can proceed as in the algebra of real numbers replacing i2 by -1 when it occurs.
1. Addition of Complex Numbers
(a+bi) + (c+di) = (a+c) + (b+d)i
Example:
z1 = 3 - 4i and z2 = -2 + 2i
z1 + z2 = (3 + (-2)) + (-4 + 2)i = 1 -2i
2. Subtraction of Complex Numbers
(a+bi) - (c+di) = (a-c)+ (b-d)i
Example:
z1 = 3 - 4i and z2 = -2 + 2i
z1 - z2 = (3 - (-2)) - (-4 - 2)i = 5 +6i
3. Multiplication of Complex Numbers
(a+bi)(c+di) = ac+bci+adi+bdi2
= (ac-bd)+(ad+bc)i
Example:
z1 = 3 - 4i and z2 = -2 + 2i
z1 ∙ z2 = (3 ∙ (-2)) + (-4 ∙ (-2))i + (3 ∙ 2)i + (-4 ∙ 2)i2 = -6 + 14i -8i2
4. Division of Complex Numbers
(a+bi)/(c+di)=(a+bi)/(c+di)×(c-di)/(c-di)
=(ac-adi+bci-bdi2)/(c2-d2i2)
=(ac+bd+(bc-ad)i)/(c2-d2i2)
=(ac+bd)/(c2+d2 )+(bc-ad)/(c2+d2) i
Example:
z1 = 3 - 4i and z2 = -2 + 2i
z1 / z2 = (3 ∙ (-2) + (-4 ∙ 2))/((-2)2 + 22) + (-4 ∙ (-2) - 3 ∙ 2)/((-2)2 + 22)i = -14/8 + (2/8)i = -7/4 + i/4
Inequalities in imaginary numbers are not defined. As for example z >0, 4 + zi < 2+4i are meaningless in complex numbers.
In real numbers, if a2 + b2=0 then a=b=0; however in complex numbers,
z12 + z22 does not imply z1 = z2 = 0
Complex conjugation: The complex conjugate of a + bi is a − bi. The importance of the complex conjugate lies in the fact that the product of a complex number and its conjugate is a real number.
(a + bi)(a − bi) = (a + b)
Additive identity: Additive identity is the complex number that represents the notion of zero for addition of complex numbers is 0 + 0i.
(a + bi) + (0 + 0i) = a + bi
Multiplicative identity: Multiplicative identity is the complex number that represents the notion of one for multiplication of complex numbers is 1+ 0i.
(a + bi)(1+ 0i) = a + bi
Example 1: Simplify (2√(-9) -3 )(3√(-16) - 1)
(2√(-9) -3 )(3√(-16) - 1)
=(2 · 3i - 3)(3 ·4i - 1)
=(6i - 3)(12i - 1)
= 72i2 – 36i – 6i + 3
= -69 – 42i
Example 2: Express in the form a + bj given 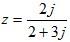
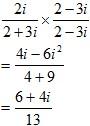
Example 3: Perform the division for the complex numbers 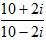
Solution: The given complex numbers are 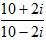
We have to reduce the denominator as well as the numerator by multiplying the numerator and denominator both by the complex number 10+2i.
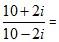
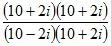
Use the formula (a+ b) (a-b) = a2- b2 to reduce the denominators. Use the formula (a+ b) 2= a2+2ab+ b2 to reduce the numerators.
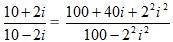
Add and also square the terms to get the values.
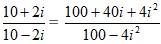
In the complex numbers the value for i2 is -1.
Substitute the value of i2 in the above equation to reduce the denominators.
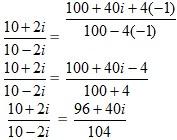
Example 4: Find the product of the complex numbers 1+ i and √ 3- i in polar form.
Solution: We can easily find that the polar form of 1+ i and √ 3- i are respectively,
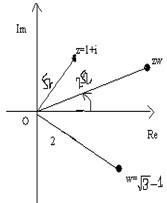
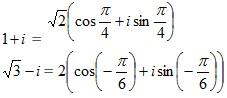
We know that z1z2 = r1r2(cos(θ1+θ2) + isin(θ1 + θ2)). This formula says that to multiply two complex numbers we need to multiply the moduli and add the arguments. Therefore multiplying 1+ i and √ 3- i using the above rule, we will get:
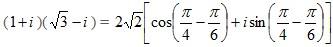
Example 5: Simplify i64,002.
Solution: i64,002 = i64,000 + 2 = i4 · 16,000 + 2 = i2 = –1.